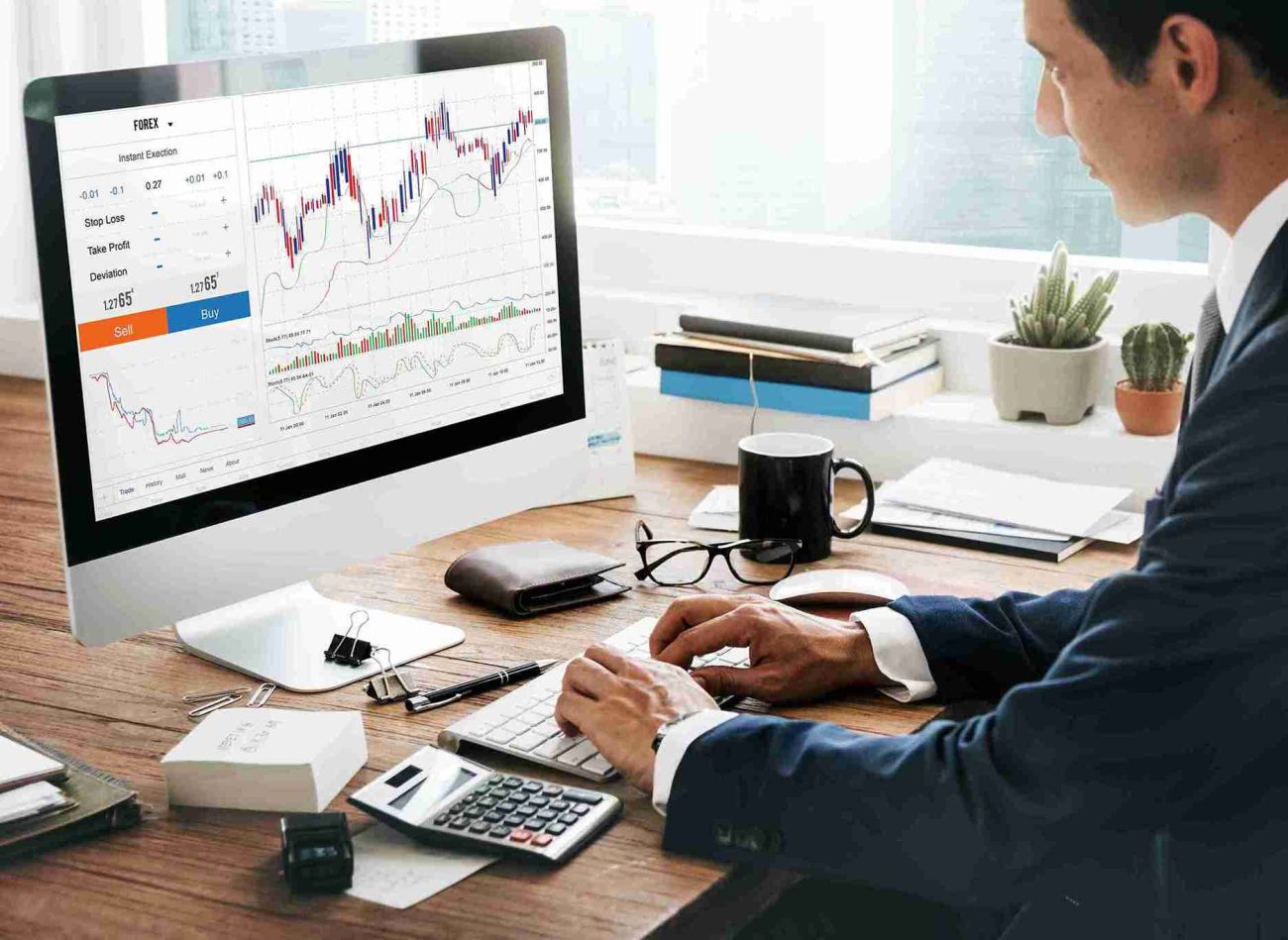
BOC digital banking has become an important topic in discussions about the transformation of financial services in the digital era. As customer expectations shift toward speed, accessibility, and security, banks are required to rethink how they deliver services. Digital banking platforms are no longer optional enhancements but core infrastructures that shape how individuals and businesses interact with financial institutions.
The Evolution of Digital Banking Services

The rise of digital banking is closely linked to changes in technology and consumer behavior. Traditional branch-based banking models were built around physical presence, paperwork, and face-to-face interactions. Over time, the adoption of online platforms, mobile applications, and automated systems redefined this structure.
Within this context, BOC digital banking represents an effort to align established banking practices with modern digital capabilities. By integrating technology into everyday financial activities, digital banking platforms aim to reduce friction, improve efficiency, and provide consistent access to services regardless of location or time.
Core Features of Modern Banking Platforms
Digital banking platforms are built around several foundational features designed to enhance user experience. These typically include account management, digital payments, fund transfers, and transaction monitoring. BOC digital banking integrates such features into a unified system that allows users to manage finances through secure digital channels.
Beyond basic transactions, modern platforms also support advanced functions such as real-time balance updates, automated notifications, and customizable account settings. These features help users maintain better financial awareness and control.
Security and Data Protection Standards
Security is a central concern in any discussion of digital financial services. As banking moves online, protecting customer data and preventing unauthorized access become critical priorities. BOC digital banking operates within structured security frameworks that include encryption, authentication protocols, and continuous monitoring.
Multi-factor authentication, secure login processes, and transaction verification are designed to reduce the risk of fraud. From an EEAT perspective, strong security practices reinforce trust and demonstrate institutional responsibility in managing sensitive financial information.
User Experience and Accessibility
Ease of use plays a significant role in the adoption of digital banking solutions. Platforms must balance advanced functionality with intuitive design to ensure accessibility for users with varying levels of technical proficiency. BOC digital banking emphasizes streamlined navigation, clear interfaces, and logical workflows.
Accessibility also extends to device compatibility. Supporting both desktop and mobile access allows customers to engage with banking services in ways that fit their daily routines. This flexibility contributes to broader financial inclusion and user satisfaction.
Digital Banking for Individuals
For individual customers, digital banking platforms simplify routine financial tasks. Activities such as checking balances, paying bills, and transferring funds can be completed without visiting a physical branch. BOC digital banking supports these everyday needs while offering tools that help users track spending and manage accounts more effectively.
Personal finance insights, transaction histories, and digital statements contribute to greater transparency. When users can easily review and understand their financial activity, they are better positioned to make informed decisions.
Support for Business and Corporate Banking
Digital transformation is equally important for business clients. Companies require efficient systems to manage payroll, supplier payments, and cash flow. BOC digital banking extends its digital infrastructure to support corporate banking needs through secure portals and integrated financial tools.
These capabilities help businesses reduce administrative overhead and improve operational efficiency. By digitizing core banking processes, organizations can focus more on strategic growth rather than manual financial management.
Integration with Financial Ecosystems
Modern banking platforms do not operate in isolation. Integration with payment networks, financial management software, and regulatory systems is essential. BOC digital banking is designed to function within a broader financial ecosystem, enabling smoother data exchange and interoperability.
Such integration supports services like digital wallets, cross-platform payments, and financial reporting. It also enhances the bank’s ability to adapt to regulatory changes and technological advancements.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance
Compliance with financial regulations remains a fundamental responsibility of any banking institution. Digital platforms must adhere to standards related to data privacy, transaction reporting, and consumer protection. BOC digital banking operates within these regulatory frameworks, ensuring that digital innovation aligns with legal and ethical requirements.
Strong governance structures support transparency and accountability. For customers, compliance provides reassurance that digital services are backed by institutional oversight rather than operating in unregulated environments.
Trust, Reputation, and Customer Confidence
Trust is a cornerstone of banking relationships. While technology enables convenience, long-term adoption depends on customer confidence. BOC digital banking builds trust through consistent service delivery, clear communication, and reliable system performance.
From an EEAT standpoint, expertise and authority are demonstrated through operational stability and adherence to industry standards. Trustworthiness is reinforced when users experience secure transactions and responsive support over time.
Digital Transformation and Banking Strategy
Digital banking initiatives are part of broader institutional strategies. Rather than simply adding online features, banks increasingly redesign processes around digital-first principles. BOC digital banking reflects this strategic shift by embedding technology into core banking functions.
This transformation supports scalability and resilience. Digital systems can adapt more quickly to changing market conditions, customer needs, and external challenges compared to traditional models.
The Role of Data and Analytics
Data plays an increasingly important role in digital banking. Transaction data, usage patterns, and customer feedback provide insights that can improve services and manage risk. BOC digital banking leverages data analytics to enhance decision-making and personalize user experiences.
Responsible data use is essential. Ethical handling of customer information, combined with transparent policies, strengthens credibility and aligns with best practices in digital finance.
Challenges in Digital Banking Adoption
Despite its advantages, digital banking adoption presents challenges. Not all users are equally comfortable with technology, and concerns about security or privacy can slow adoption. BOC digital banking addresses these challenges through education, support resources, and gradual feature implementation.
Infrastructure reliability is another consideration. Digital platforms must maintain uptime and performance to meet customer expectations. Continuous investment in technology and maintenance is necessary to sustain service quality.
Future Trends in Digital Banking
The future of digital banking is shaped by innovation in areas such as artificial intelligence, automation, and real-time payments. BOC digital banking is positioned within this evolving landscape, where personalization and efficiency are expected to increase.
Emerging trends include smarter financial assistants, predictive analytics, and deeper integration with non-banking services. While technology will continue to evolve, the fundamental goal remains the same: providing secure, reliable, and accessible financial services.
Conclusion
BOC digital banking illustrates how traditional banking institutions can adapt to the demands of a digital economy. By combining secure technology, user-focused design, and regulatory compliance, digital banking platforms redefine how financial services are delivered.
As individuals and businesses increasingly rely on digital channels, understanding the structure and role of such platforms becomes essential. Through responsible innovation and continued investment, digital banking solutions can support long-term financial stability and customer trust in an ever-changing financial landscape.